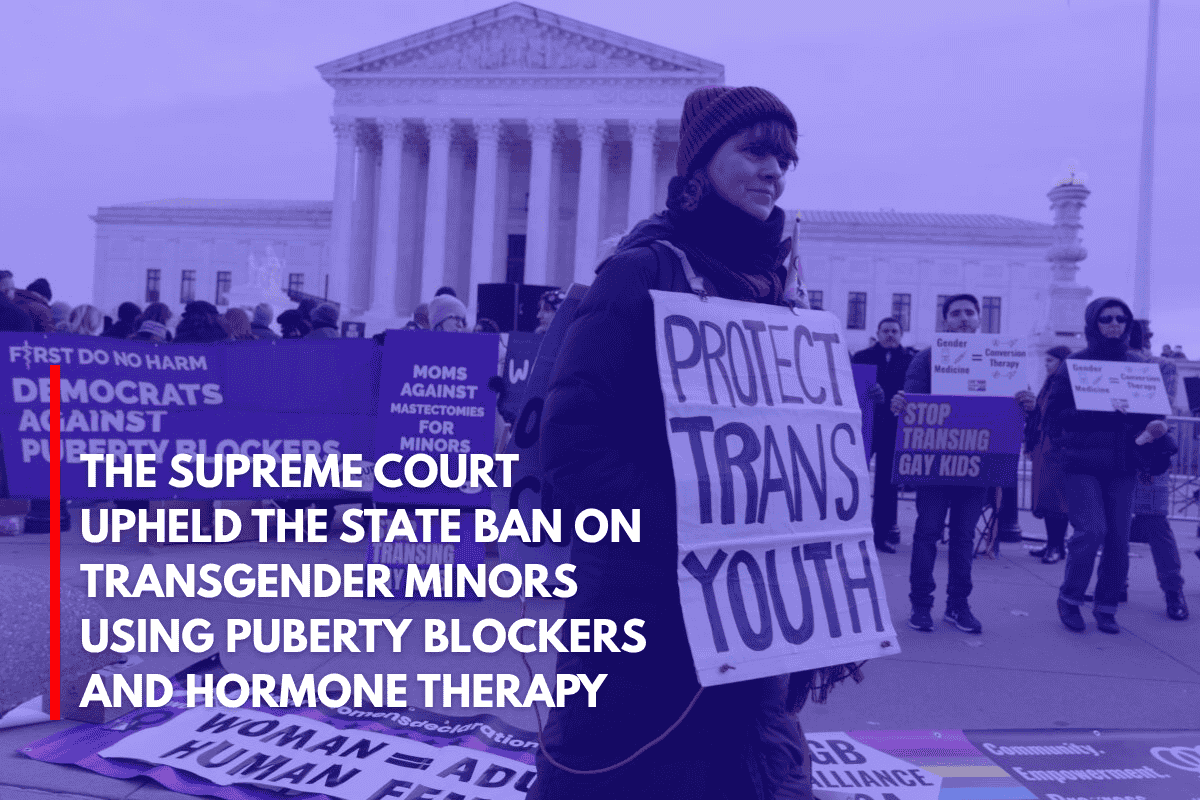
Washington, D.C. – In a 6-3 decision on June 18, 2025, the U.S. Supreme Court upheld Tennessee’s ban on gender-affirming care for minors, a significant setback for transgender Americans who have increasingly faced opposition from conservative states.
The case, one of the court’s most high-profile decisions this year, comes five years after the court ruled in favor of transgender rights in the workplace under a landmark civil rights law.
The Court’s Ruling
The court’s majority, consisting of six conservative justices, concluded that the Tennessee law, which prohibits minors from accessing puberty blockers and hormone therapy, does not violate the equal protection clause of the 14th Amendment.
Chief Justice John Roberts wrote the majority opinion, stating, “Having concluded it does not, we leave questions regarding its policy to the people, their elected representatives, and the democratic process.”
However, the three liberal justices, including Justice Sonia Sotomayor, dissented strongly. Sotomayor criticized the decision, claiming the court “retreats from meaningful judicial review” and “abandons transgender children and their families to political whims.” She read part of her dissent from the bench, a rare and notable move in order to emphasize her disapproval.
Reaction from Tennessee and Opponents
Tennessee’s Attorney General Jonathan Skrmetti hailed the decision as a “landmark victory,” claiming it was necessary to protect children from decisions they might not fully understand.
He emphasized that a bipartisan supermajority in Tennessee’s legislature had carefully considered the evidence before enacting the law. Skrmetti also argued that the law does not discriminate against transgender people but is instead designed to safeguard young people from irreversible medical decisions.
On the other hand, Chase Strangio, a lawyer for the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) who represented the families challenging the law, described the ruling as a “painful setback” for transgender rights.
Strangio noted that while this was a blow, there are still avenues to fight against other restrictions on transgender people’s rights, particularly in light of actions taken by the Trump administration and states with similar bans.
Discrimination Concerns and Legal Arguments
One of the core issues at stake was whether the law discriminates against transgender minors. The Biden administration and the families challenging the law argued that the law creates unequal treatment based on gender.
For instance, a teenager assigned male at birth might be allowed testosterone for delayed puberty, but a teen assigned female at birth who needs testosterone to treat gender dysphoria would be denied. This, they argued, violates the equal protection clause by denying care to transgender minors that cisgender minors would receive.
However, Tennessee’s defense argued that the treatments have different risks and benefits depending on the individual, and that this policy is necessary to protect children from making life-altering decisions before they fully understand the consequences.
Impact on Transgender Rights
The decision is particularly concerning for transgender advocacy groups because it signals that similar bans on gender-affirming care in other states could also withstand legal challenges. This ruling also signals that states may have broader legislative flexibility in regulating medical care, including gender-affirming treatments, for minors.
Despite the setback, transgender rights advocates, including Strangio, continue to fight against these measures, claiming that the rights of transgender minors should not be subject to political influence.
Medical Support for Gender-Affirming Care
Gender-affirming care for minors is supported by many of the nation’s leading medical organizations, including the American Medical Association, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the American Psychiatric Association, all of which stress that such care is essential for the well-being of transgender youth.
However, the court’s conservative justices pointed to debates in some European countries, such as England, where the National Health Service has restricted the use of certain gender-affirming treatments. The justices argued that these international developments highlight the need for more research and legislative decision-making in this area.
The Path Forward
The case, U.S. v. Skrmetti, is likely to have a lasting impact on transgender rights and the legality of gender-affirming care for minors across the country. Although this ruling only directly affects Tennessee, its effects are expected to ripple across the U.S., especially in the growing number of states enacting similar laws.
Transgender advocates have vowed to continue their fight for the rights of transgender minors, emphasizing that the battle is far from over despite this setback. Legal challenges to other state laws and policies, as well as future appeals, are likely to shape the future of transgender rights in the U.S.









Leave a Reply